Assemble Tutorial¶
Important!!! This tutorial assumes you have access to a complete cMonkey2 ensemble.
In a nutshell¶
The ASSEMBLE scripts transfer and compile individual cMonkey2 SQLite databases into an integrated MongoDB database.
In addition, they perform several post-processing steps, including: detection of gene regulatory elements (GREs) by comparing individual bicluster motifs with TOMTOM and clustering with MCL, genome-wide scanning of motifs with FIMO, and detection of co-regulated modules or corems using link-community detection.
Requirements¶
- MongoDB >= 2.4.9
- compiled C++ scripts for corem detection, available here
IMPORTANT: This tutorial currently assumes that TOMTOM, MCL and FIMO have already been run.
A single GRE definition file is read from, eg:
/ensemble-head-dir
/out.mot_metaclustering.txt.I45.txt
FIMO scans are read from each run sub-directory, eg:
/ensemble-head-dir
/org-out-xxx
/fimo-outs
/fimo-out-xxxx.bz2
Optional:
row_annot: tab-delimited row (gene) annotations. Will be downloaded from MicrobesOnline automatically using--ncbi_codeif undefinedcol_annot: tab-delimited column (condition) annotations.
The format for these files will be described in detail below.
Additionally, the Python modules described on the Home page are required to run these scripts.
Scripts¶
egrin2-assemble: The control function for ASSEMBLE scripts.makeCorems.py: Identifies corems using C++ scripts compiled aboveresample_QSub.py: Generates QSub script for submission of resamples to clustersql2mongoDB.py: Merges individual cMonkey SQLite dbs and post-processing data into MongoDB
$ egrin2-assemble -h
usage: egrin2-assemble [-h] --organism ORGANISM --ratios RATIOS
[--targetdir TARGETDIR] [--backbone_pval BACKBONE_PVAL]
[--cores CORES] [--link_comm_score LINK_COMM_SCORE]
[--link_comm_increment LINK_COMM_INCREMENT]
[--link_comm_density_score LINK_COMM_DENSITY_SCORE]
[--corem_size_threshold COREM_SIZE_THRESHOLD]
[--n_resamples N_RESAMPLES]
[--cluster_arch CLUSTER_ARCH] [--sge_user SGE_USER]
[--dbengine DBENGINE] [--host HOST] [--port PORT]
[--targetdb TARGETDB] [--prefix PREFIX]
[--ensembledir ENSEMBLEDIR] [--col_annot COL_ANNOT]
[--row_annot ROW_ANNOT]
[--row_annot_match_col ROW_ANNOT_MATCH_COL]
[--gre2motif GRE2MOTIF] [--genome_annot GENOME_ANNOT]
[result_dbs [result_dbs ...]]
assemble.py - prepare cluster runs
positional arguments:
result_dbs
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--organism ORGANISM 3 letter organism code
--ratios RATIOS Path to ratios file. Should be 'raw' (normalized)
ratios, not the standardized ratios used by cMonkey
--targetdir TARGETDIR
Storage path for MongoDB and corem data
--backbone_pval BACKBONE_PVAL
Significance pvalue for gene-gene backbone. Default =
0.05.
--cores CORES Number local cores to use for corem C++ scripts
--link_comm_score LINK_COMM_SCORE
Scoring metric for link communities
--link_comm_increment LINK_COMM_INCREMENT
Height increment for cutting agglomerative clustering
of link communities
--link_comm_density_score LINK_COMM_DENSITY_SCORE
Density score for evaluating link communities
--corem_size_threshold COREM_SIZE_THRESHOLD
Defines minimum corem size. Default = 3.
--n_resamples N_RESAMPLES
Number resamples to compute for corem condition
assignment. Default = 10,000
--cluster_arch CLUSTER_ARCH
where to run resampling on
--sge_user SGE_USER Cluster user name
--dbengine DBENGINE mongodb or sqlite
--host HOST MongoDB host. Default 'localhost'
--port PORT MongoDB port
--targetdb TARGETDB Optional ensemble MongoDB database name
--prefix PREFIX Ensemble run prefix. Default: *organism*-out-
--ensembledir ENSEMBLEDIR
Path to ensemble runs. Default: cwd
--col_annot COL_ANNOT
Tab-delimited file with experiment annotations
--row_annot ROW_ANNOT
Optional row (gene) annotation tab-delimited file. If
not specified, annotations will be downloaded from
MicrobesOnline using --ncbi_code.
--row_annot_match_col ROW_ANNOT_MATCH_COL
Name of column in row_annot that matches row names in
ratios file.
--gre2motif GRE2MOTIF
Motif->GRE clustering file
--genome_annot GENOME_ANNOT
Optional genome annotation file. Automatically
downloaded from MicrobesOnline using --ncbi_code
ASSEMBLE an EGRIN 2.0 ensemble¶
In this tutorial we will see how you would ASSEMBLE an Escherichia coli EGRIN 2.0 ensemble using several example files and a couple of cMonkey2 runs, which we provide here.
STEP 1: Generate optional input files¶
First, let’s explore the optional annotation files. Providing annotations for genes and conditions is a great way to enrich your analysis of the ensemble. You can get a better idea for the utility of these metainformation by following the advanced mining tutorial
row_annot¶
As noted above, the row_annot file will be downloaded automatically from MicrobesOnline if a custom annotation is not provided. If you provide your own row_annot file, however, you will also need to specificy --row_annot_matchCol, which is the name of the column in your annotation file that matches the gene name used by cMonkey2 (i.e. the row names in your ratios file).
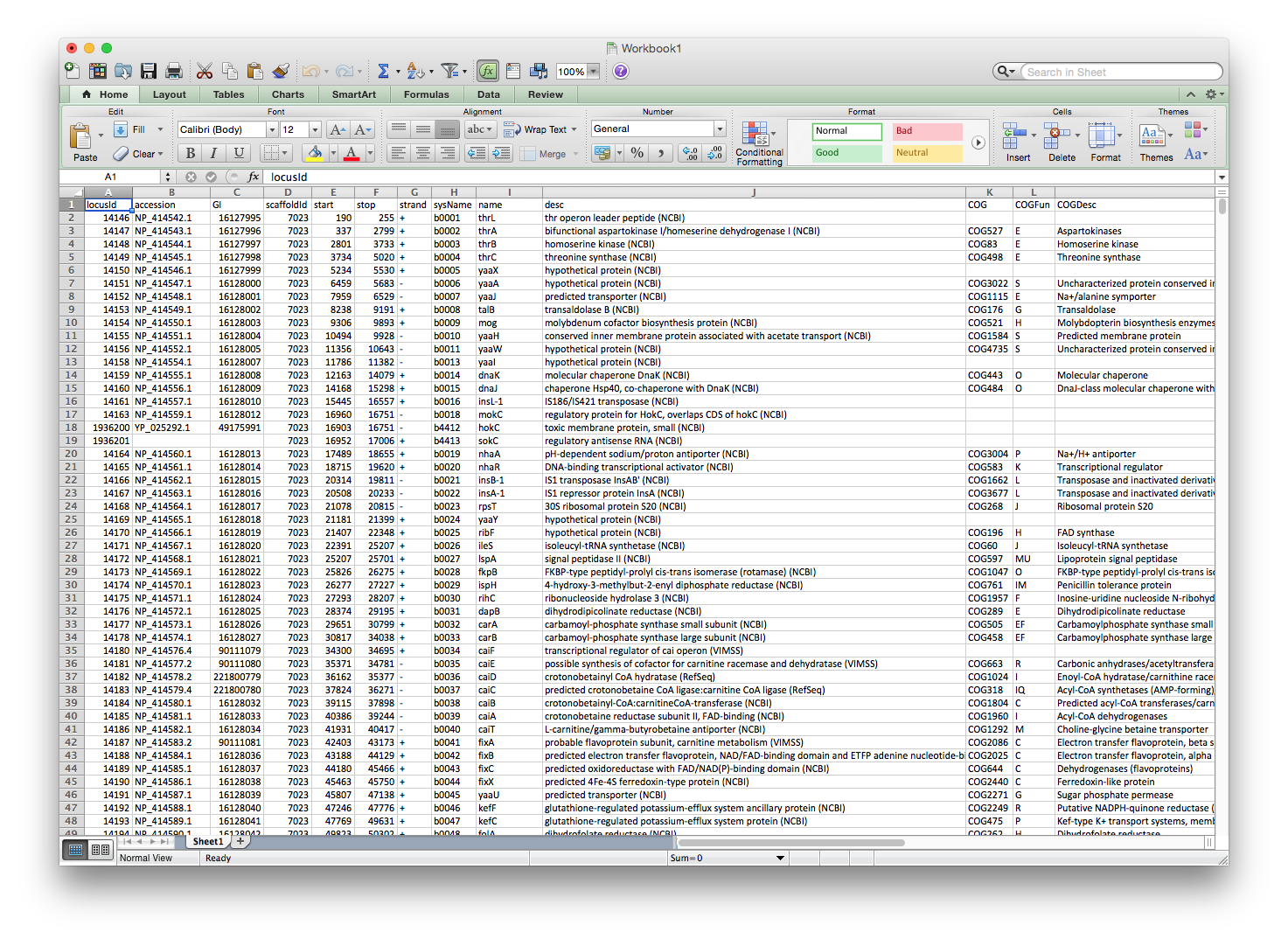
The row annotation file should look like the annotation file supplied by MicrobesOnline, where each row specifies a gene and each of the columns specifies some information about that gene. Again, you must ensure that at least one of the columns contains gene names that match the gene names in the ratios file used by cMonkey2, in the case of MicrobesOnline, it is the sysName column.
Here is an example annotation fil e for E. coli direct from MicrobesOnline, the file itself is available here.
col_annot¶
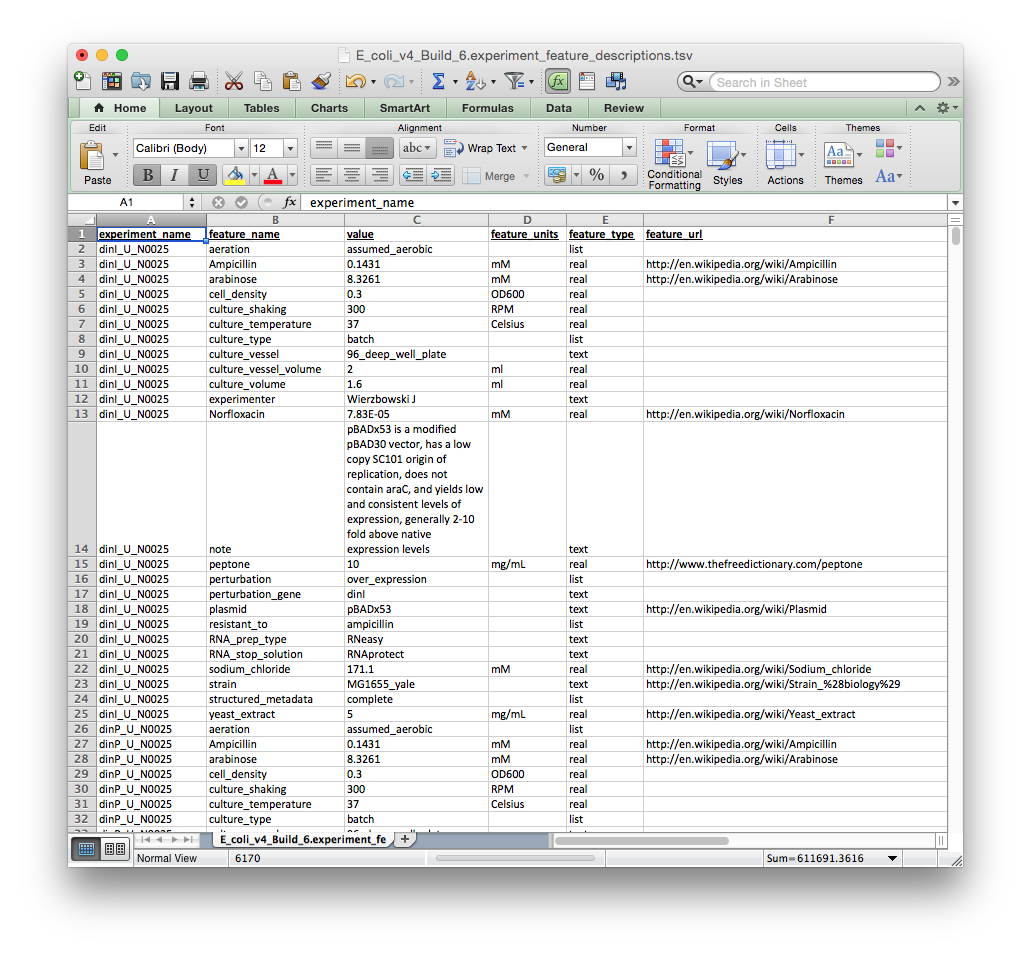
The col_annot file provides metainformation about each experiment. Like the row_annot file, these annotations are optional, but they can be valuable for making sense of ensemble predicitions.
Please note that the file format is different here. Each row contains a particular experimental meta-annotation followed by several required descriptions: (1) experiment_name, (2) feature_name, (3) value, (4) feature_units, (5) feature_type. The experiment_name column should match the experiment name in the ratios file.
The col_annot file should look like the tab-delimited file depicted below. You can download an E. coli col_annot file to use as a template here
STEP 2: Run egrin2-assemble¶
Important!!! TOMTOM, MCL, and FIMO should be run prior to assembly. Otherwise the ensemble will not contain GREs or motif scans.
To run the assembler, you must supply several files. At a minimum, you should supply:
--organism: 3 letter organism code--ratios: Path to ratios file. Should be ‘raw’ (normalized) ratios, not the standardized ratios used by cMonkey--targetdir: Storage path for MongoDB and corem data
Note: The MongoDB engine has been replaced in favor of storing data in sqlite because it does not require a running database server. Furthermore the assembly step does not require a cluster anymore
$ egrin2-assemble --organism mtu --ratios <ratios file> --targetdir <output directory> --targetdb <output database name>
This will run the entire assembly step